SHA-256 and bitcoin mining
There is a lottery in bitcoin network that takes place every ~10 minutes. The lottery winner submits a new block to blockchain (if the majority of the network agrees with it) and awards with bitcoins (25 initally, halve every 210000 blocks or ~4 years). The winner is someone who was first to find a nonce (a number) that beeing concatenated with some other data (including previous block hash and timestamp) results in a hash function output smaller than some value (difficulty, adjusts every ~2 weeks in order to keep the time needs to resolve the task in about 10 minutes).
What to hash:
- version:
0x20000000 - reversed previous block hash
- transactions (reversed Merkle tree root)
- timestamp
- nonce
block_hash = sha256(sha256( version + reversed(prev_block) + reversed(mrkl_root) + timestamp + bits + nonce ))
An example using python
Took a block from the blockchain:
Previous block: 00000000000000000146161cdb757ffc5a8b22dff06b27a76f6f7d0584f5df05
Hash: 00000000000000000244bf1d3600aada272d2d08aa1919a88ba9ecd14f42f3ae
Merkle root: 536e129807282bf22dcb0c169dc0e5cfeb47dac85c7afde3afb2e0fb02161076
Timestamp: 2016-09-27 13:38:38 (0x57ea765e)
Bits: 402951892 (0x18048ed4)
Nonce: 2612046070 (0x9bb0a8f6)
bits = 0x18048ed4 exp = bits >> 24 # 0x18 mant = bits & 0xffffff # 0x48ed4 target_hexstr = '%064x' % (mant * (1<<(8*(exp - 3)))) # '0000000000000000048ed4000000000000000000000000000000000000000000'
import hashlib import struct import binascii sha256 = hashlib.sha256 block = ( struct.pack('<L', 0x20000000) + bytes.fromhex('00000000000000000146161cdb757ffc5a8b22dff06b27a76f6f7d0584f5df05')[::-1] + bytes.fromhex('536e129807282bf22dcb0c169dc0e5cfeb47dac85c7afde3afb2e0fb02161076')[::-1] + struct.pack('<LLL', 0x57ea765e, 0x18048ed4, 0x9bb0a8f6) ) first_hash = sha256(block).digest() second_hash = sha256(first_hash).digest() print(binascii.b2a_hex(block)) print(binascii.b2a_hex(first_hash[::-1])) print(binascii.b2a_hex(second_hash[::-1])) # b'0000002005dff584057d6f6fa7276bf0df228b5afc7f75db1c164601000000000000000076101602fbe0b2afe3fd7a5cc8da47ebcfe5c09d160ccb2df22b280798126e535e76ea57d48e0418f6a8b09b' # b'57e9fff3d914c07dd4eadc189887cbcc0ead44bc0e753c6ee963e59e618b215d' # b'00000000000000000244bf1d3600aada272d2d08aa1919a88ba9ecd14f42f3ae'
SHA-256
This code has been written just for fun, it is slow and may produce inaccurate results.
The idea was to transition from mathematics to an algorithm.
sha256.py gist on GitHub.
import binascii import hashlib import itertools def int_to_list(n): return [int(i) for i in '{:32b}'.format(n).replace(' ', '0')] def list_to_int(l): s = 0 c = 1 for i in reversed(l): s += i * c c *= 2 return s def list_to_digest(binary): res = b'' for i in range(0, len(binary), 8): res += list_to_int(binary[i: i + 8]).to_bytes(1, byteorder='big') return res def bin_maj(*parts): res = [] for i in range(0, 32): s = 0 for part in parts: s += part[i] res.append(1 if s > len(parts) // 2 else 0) return res def bin_rrot(a, shift): return a[-shift:] + a[:-shift] def bin_rshift(a, shift): return (shift * [0]) + list(a[:-shift]) def bin_xor(*parts): res = [] for i in range(0, len(parts[0])): s = 0 for part in parts: s += part[i] res.append(1 if s % 2 == 1 else 0) return res def bin_ch(n, l1, l2): res = [] for i in range(0, len(n)): res.append(l1[i] if n[i] else l2[i]) return res def bin_sum(*parts): res = [] mov = 0 for i in range(0, len(parts[0])): s = 0 for p in parts: s += p[-i-1] s += mov res.append(s % 2) mov = s // 2 res.reverse() return res[-32:] def to_chunks(iterable, n=512): it = iter(iterable) while True: chunk = tuple(itertools.islice(it, n)) if not chunk: return yield chunk # Provided by NSA _k = ( 0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2 ) _h = ( 0x6a09e667, 0xbb67ae85, 0x3c6ef372, 0xa54ff53a, 0x510e527f, 0x9b05688c, 0x1f83d9ab, 0x5be0cd19 ) def preprocess(data_str): data_bin = [] for c in data_str: for i in '{:8b}'.format(c).replace(' ', '0'): data_bin.append(int(i)) data_bin.append(1) while len(data_bin) % 512 != 448: data_bin.append(0) for i in '{:64b}'.format(len(data_str) * 8).replace(' ', '0'): data_bin.append(int(i)) return data_bin def sha256(data): a0, b0, c0, d0, e0, f0, g0, h0 = map(int_to_list, _h) for chunk in to_chunks(preprocess(data), n=512): w = [0] * 64 w[0:16] = to_chunks(chunk, n=32) for i in range(16, 64): s0 = bin_xor(bin_rrot(w[i-15], 7), bin_rrot(w[i-15], 18), bin_rshift(w[i-15], 3)) s1 = bin_xor(bin_rrot(w[i-2], 17), bin_rrot(w[i-2], 19), bin_rshift(w[i-2], 10)) w[i] = bin_sum( w[i-16], s0, w[i-7], s1 ) a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = a0, b0, c0, d0, e0, f0, g0, h0 for i in range(0, 64): sum1 = bin_sum( w[i], int_to_list(_k[i]), h, bin_ch(e, f, g), bin_xor(bin_rrot(e, 6), bin_rrot(e, 11), bin_rrot(e, 25)) ) sum2 = bin_sum( bin_xor(bin_rrot(a, 2), bin_rrot(a, 13), bin_rrot(a, 22)), bin_maj(a, b, c), sum1 ) a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = sum2, a, b, c, bin_sum(d, sum1)[-32:], e, f, g a0 = bin_sum(a0, a) b0 = bin_sum(b0, b) c0 = bin_sum(c0, c) d0 = bin_sum(d0, d) e0 = bin_sum(e0, e) f0 = bin_sum(f0, f) g0 = bin_sum(g0, g) h0 = bin_sum(h0, h) return a0 + b0 + c0 + d0 + e0 + f0 + g0 + h0 if __name__ == '__main__': assert binascii.b2a_hex(list_to_digest(sha256(''))) == b'e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855' block = b'0000002005dff584057d6f6fa7276bf0df228b5afc7f75db1c164601000000000000000076101602fbe0b2afe3fd7a5cc8da47ebcfe5c09d160ccb2df22b280798126e535e76ea57d48e0418f6a8b09b' assert list_to_digest(sha256(block)) == hashlib.sha256(block).digest()
Optimizations
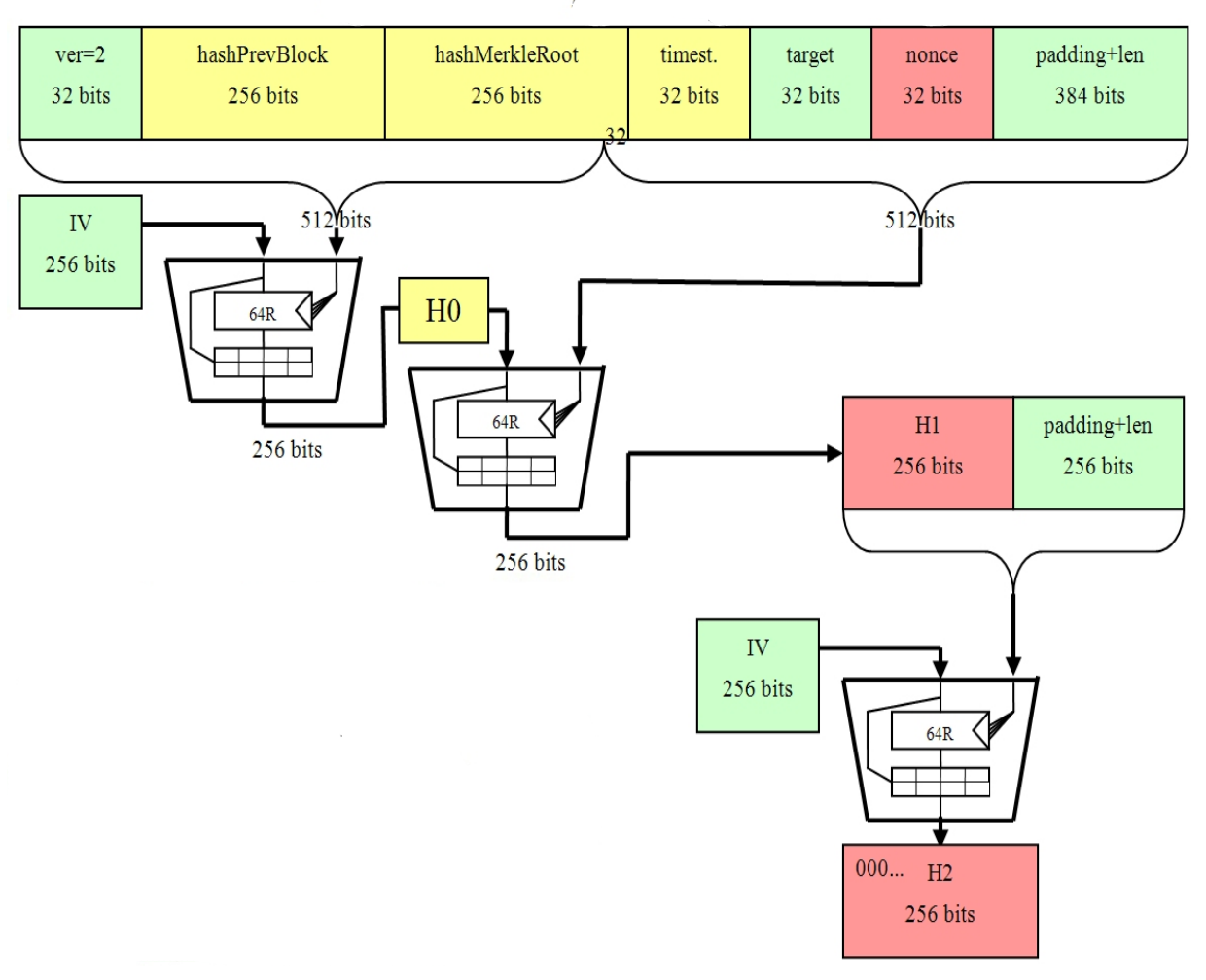
On the image:
- green: fixed data
- yellow: changes slowly (for each new block)
- red: changes frequently
One may notice that if we manipulate only nonce we may reuse results of the first computation.
Here we omit sha256 computation of first message parts for all nonce except the first one:
import struct class Miner(): def __init__(self, previous_hash, transactions_hash, timestamp, bits, nonces): self.previous_hash = previous_hash self.transactions_hash = transactions_hash self.timestamp = timestamp self.bits = bits self.nonces = nonces _h = ( 0x6a09e667, 0xbb67ae85, 0x3c6ef372, 0xa54ff53a, 0x510e527f, 0x9b05688c, 0x1f83d9ab, 0x5be0cd19 ) _k = ( 0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2 ) @staticmethod def rrot(v, shift): return ((v >> shift) | (v << (32-shift))) & 0xFFFFFFFF @staticmethod def ch(a, b, c): return (a & b) ^ ((~a) & c) @staticmethod def maj(a, b, c): return (a & b) ^ (a & c) ^ (b & c) @classmethod def get_w(cls, block): w = [0] * 64 w[0:16] = [(block >> (480 - i * 32)) & 0xffffffff for i in range(0, 16)] for i in range(16, 64): w[i] = ( w[i-16] + (cls.rrot(w[i-15], 7) ^ cls.rrot(w[i-15], 18) ^ (w[i-15] >> 3)) + w[i-7] + (cls.rrot(w[i-2], 17) ^ cls.rrot(w[i-2], 19) ^ (w[i-2] >> 10)) ) & 0xffffffff return w @classmethod def iteration(cls, w, k, a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h): s = (w + k + h + cls.ch(e, f, g) + (cls.rrot(e, 6) ^ cls.rrot(e, 11) ^ cls.rrot(e, 25))) & 0xffffffff a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = ( ((cls.rrot(a, 2) ^ cls.rrot(a, 13) ^ cls.rrot(a, 22)) + cls.maj(a, b, c) + s) & 0xffffffff, a, b, c, (d + s) & 0xffffffff, e, f, g ) return a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h def run(self): pack = ( struct.pack('<L', 0x20000000) + bytes.fromhex(self.previous_hash)[::-1] + (bytes.fromhex(self.transactions_hash)[::-1])[:-4] ) block = 0 for i in pack[:512]: block = (block << 8) | i w = self.get_w(block) sha1 = list(self._h) for i in range(0, 64): sha1 = self.iteration(w[i], self._k[i], *sha1) sha1 = [(sha1[i] + self._h[i]) & 0xffffffff for i in range(0, 8)] results = [] for nonce in self.nonces: pack = ( (bytes.fromhex(self.transactions_hash)[::-1])[-4:] + struct.pack('<LLL', self.timestamp, self.bits, nonce) + struct.pack('>LLLLLLLLLLLL', 0x80000000, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 640) ) block = 0 for i in pack[:512]: block = (block << 8) | i w = self.get_w(block) sha2 = list(sha1) for i in range(0, 64): sha2 = self.iteration(w[i], self._k[i], *sha2) sha2 = [((sha2[i] + sha1[i]) & 0xffffffff) for i in range(0, 8)] block = 0 for i in range(0, 8): block = block << 32 | sha2[i] block = (block << 256) | (1 << 255) | 256 w = self.get_w(block) sha3 = list(self._h) for i in range(0, 64): sha3 = self.iteration(w[i], self._k[i], *sha3) sha3 = [(sha3[i] + self._h[i]) & 0xffffffff for i in range(0, 8)] result = 0 for i in struct.pack('>LLLLLLLL', *sha3)[::-1]: result = (result << 8) | i results.append(result) return results if __name__ == '__main__': previous_hash = '00000000000000000146161cdb757ffc5a8b22dff06b27a76f6f7d0584f5df05' transactions_hash = '536e129807282bf22dcb0c169dc0e5cfeb47dac85c7afde3afb2e0fb02161076' timestamp = 1474983518 bits = 0x18048ed4 nonces = [ 0x9bb0a8f6, 0xabb0a8f6 ] assert Miner(previous_hash=previous_hash, transactions_hash=transactions_hash, timestamp=timestamp, bits=bits, nonces=nonces ).run() == [ 55624467632295270487489375918890129241800824638908068782, 75916835553102774891823884113900634385218467396093025039177034268615350443547 ]
It gives us about 30% efficiency increase. We may still improve the algorithm for a few more percents (see The Unreasonable Fundamental Incertitudes Behind Bitcoin Mining).
Hardware
Mining with CPU: ~4000W / GH.
Mining with GPU: ~210W / GH (Radeon 7790).
Mining with FPGA (45nm): ~50W / GH.
Mining with ASIC (16nm): ~0.1W / GH, 14TH/s (ANTMINER S9, 12 June 2016 model).
Vocabulary
Big and small endian
Endianness is the order of the bytes that compose a digital word in computer memory. When storing a word in big-endian format the most significant byte, which is the byte containing the most significant bit, is stored first.
See python struct Byte Order, Size, and Alignment.
import struct import binascii binascii.b2a_hex(struct.pack('<L', 10)) # little-endian # b'0a000000' binascii.b2a_hex(struct.pack('>L', 10)) # big-endian # b'0000000a'
L - unsigned long, 4 bites.
Hash digest
Accrding to hashlib - Secure hashes and message digests:
Return the digest of the data passed to the update() method so far. This is a bytes object of size digest_size which may contain bytes in the whole range from 0 to 255.
Links
Bitcoin mining the hard way: the algorithms, protocols, and bytes, Ken Shirriff's blog
pysha2 by thomdixon on GitHub
Mining Bitcoin with pencil and paper: 0.67 hashes per day on Ken Shirriff's blog
Endianness on Wikipedia
SHA-2 on Wikipedia
The Unreasonable Fundamental Incertitudes Behind Bitcoin Mining paper by Nicolas T. Courtois, Marek Grajek and Rahul Naik